Unlocking Discoveries: Your Guide to the DeSci Crypto Movement

DeSci (decentralized science) brings blockchain into science to improve funding, data sharing, and collaboration.
On this page
- What Does Decentralized Science (DeSci) Mean?
- Rethinking Science: DeSci vs. Traditional Approaches
- Funding
- Peer Review
- Academic Publishing
- Data Storage and Ownership
- The Role of Blockchain in Decentralized Science
- The Ecosystem of DeSci: Projects and Communities
- Where Is Decentralized Science Headed Next?
Traditional science faces big challenges like lack of transparency, limited trust, poor collaboration, and issues around intellectual property rights for discoveries. DeSci, short for decentralized science, is a movement using blockchain technology to transform how research is done.
Read on to learn more about DeSci and its use cases.
What Does Decentralized Science (DeSci) Mean?
Blockchain technology includes various applications, and DeSci is one of them. In a broad sense, DeSci refers to the use of blockchain to create a more transparent and accountable scientific ecosystem. There are different interpretations of the question “What is DeSci?” According to Ethereum Foundation:
Decentralized science (DeSci) is a movement that aims to build public infrastructure for funding, creating, reviewing, crediting, storing, and disseminating scientific knowledge fairly and equitably using the Web3 stack.
The Web3 stack mentioned here includes technologies such as blockchain, cryptocurrencies, smart contracts, NFTs (non-fungible tokens), and DAOs (decentralized autonomous organizations) – all of which support the core idea behind DeSci.
DeSci crypto projects vary in purpose and use cases. Many of them issue or use crypto tokens that serve purposes like research funding, platform payments, and contributor rewards. For example, with DeSci crypto tokens, researchers can raise funds directly from the community, bypassing closed institutions and traditional grant systems.
Over the past few years, the field has been gaining traction and attracting the attention of builders and founders, including Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin and former Binance CEO Changpeng Zhao (CZ).
Rethinking Science: DeSci vs. Traditional Approaches
Decentralized technologies are part of digital innovation in science. What’s known as traditional or centralized science has been evolving, but many issues still remain unsolved. DeSci offers new ways to address these challenges. Here are some key aspects that set descience apart from traditional scientific practices.
Funding
Lack of transparency in funding is one of the main issues in traditional science. Decisions are often made behind closed doors by institutions or governments, with little explanation of why certain projects are chosen. This creates a trust gap since funding sources and research independence aren’t always clear.
DeSci offers an alternative through decentralized technologies, where control and decision-making are distributed among participants rather than concentrated in a single authority. It largely relies on DAOs that use smart contracts and governance tokens to enable transparent funding and community-driven priorities. Typically, DAOs support research areas that lack sufficient traditional funding.
Peer Review
In traditional science, peer review – the process where experts evaluate a research paper – can be slow and unclear. Reviewers usually volunteer their time without pay, which sometimes causes delays and allows biases to sneak in. This lack of transparency also makes it hard to ensure that experiments can be reproduced and results verified by others. DeSci offers a new way forward. It opens up peer review to the community, rewarding reviewers with tokens to encourage honest and timely feedback. By recording every step on the blockchain, DeSci creates a transparent, trustworthy process that not only checks research thoroughly but also supports reproducibility, so others can reliably repeat and build upon the work.
Academic Publishing
Research papers and data are often hidden behind expensive paywalls, meaning only those who can afford subscriptions can access them. This makes it harder for scientists to collaborate or for the public to benefit from new discoveries. DeSci helps remove these barriers, enabling a more inclusive and collaborative approach. Regardless of their location, researchers can connect and contribute to shared projects in real-time through decentralized platforms. Focusing on openness and transparency, DeSci uses blockchain to create permanent, public records of research, making data and papers available to everyone.
Data Storage and Ownership
Traditionally, scientific knowledge and data are stored in ways that restrict access to a select few. Data and ideas are usually kept by large institutions. Research results and data are stored on private servers, meaning only certain people can access them. These institutions often own patents and copyrights, so individual researchers don’t have full control. This can make sharing and using the data complicated. DeSci changes this by storing data on a decentralized network that everyone can access and trust. Researchers have more control over their work through tools like IP-NFTs (Intellectual Property NFTs), which prove who owns the data and when it was created. This way, creators can share or license their work however they want.
The Role of Blockchain in Decentralized Science
Blockchain is the backbone of DeSci. Before the creation of Bitcoin and modern blockchain networks, scientists had already taken steps toward open access to research. The Open Access movement gained momentum in the late 1990s with the aim of making research articles across various academic fields available online. In 1991, for example, Paul Ginsparg founded arXiv, a research-sharing platform.
Although the Open Access movement made science more publicly available, issues related to funding, intellectual property, and transparency remained unsolved.
The launch of Bitcoin in 2009 marked a turning point. It introduced the idea of a decentralized, trustless system where value and information could be exchanged without middlemen. Transactions once added to the blockchain can’t be altered, making them trustworthy and permanently verifiable. A network of independent nodes secures the system, processes transactions, and changes how data is stored and verified.
In 2015, Ethereum took this further by enabling smart contracts – self-executing programs that run on the blockchain. Smart contracts expanded blockchain’s use beyond financial transactions. Decentralized science crypto projects emerged to build on the values of open science, using blockchain to automate funding, licensing, and collaboration in research. With DeSci, researchers can prove ownership of their work, receive funding directly from the community, and store data in decentralized networks that anyone can access and verify.
The Ecosystem of DeSci: Projects and Communities
DeSci is one of the fastest-growing sectors in blockchain. According to Messari, 50% of the top DeSci projects were launched in 2024. These projects provide tools and platforms that enable a more open, collaborative, and equitable scientific future. Based on their purpose, they fall into funding, ecosystems, infrastructure, communities, and other categories.
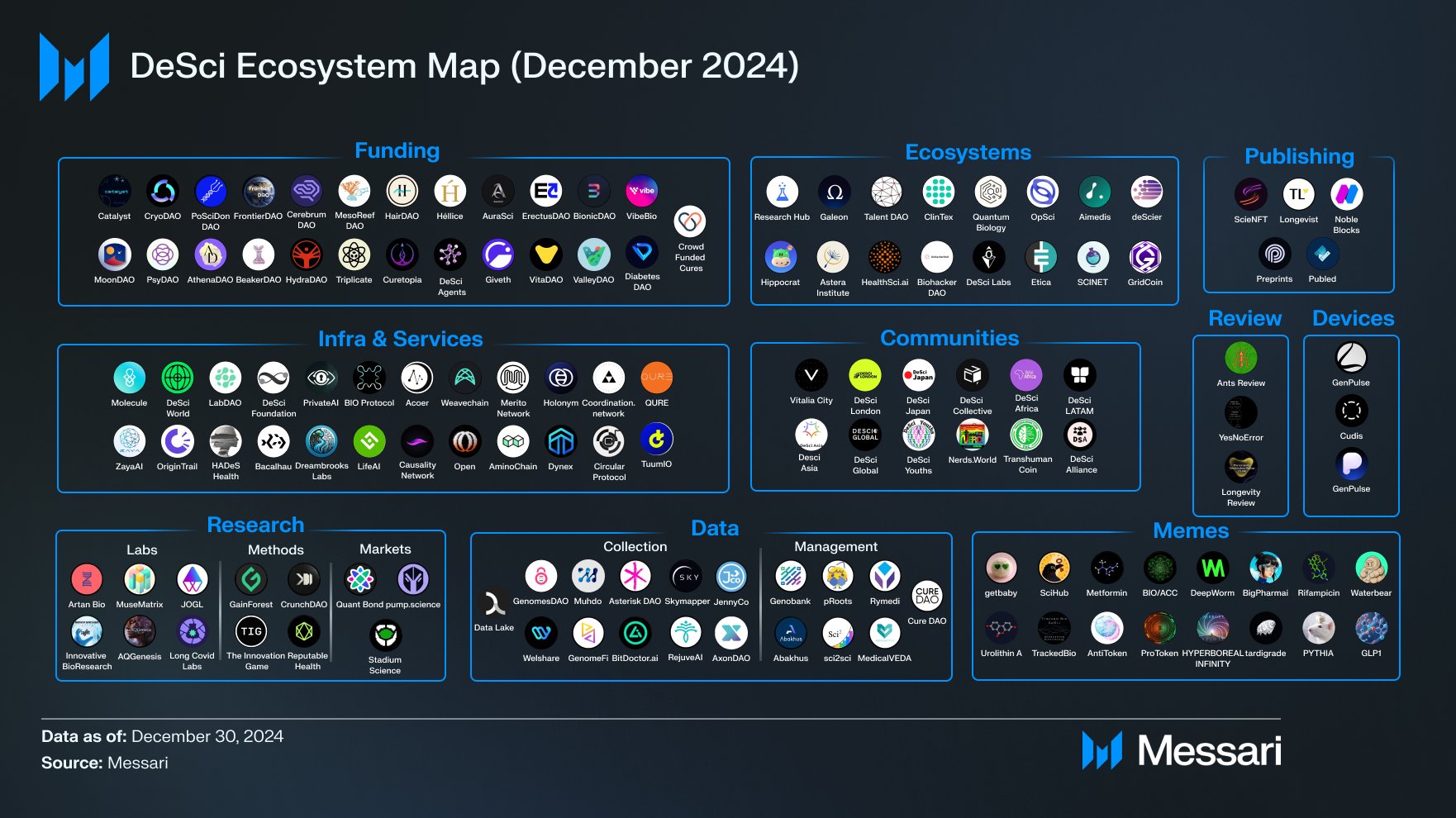
As of July 23, 2025, total market cap of DeSci tokens is above $711 million, according to CoinGecko. These assets incentivize participation, governance of these platforms, and fund research. Among the most popular DeSci projects are:
- Molecule: Founded in 2020, Molecule is a decentralized biotech protocol focused on building infrastructure for funding and tokenizing intellectual property. Researchers and developers can use the platform to launch, manage, and grow projects on-chain. In 2024, Molecule launched Catalyst, a platform designed to fund research and engage the community through IP tokens.
- OriginTrail: This is a DeSci ecosystem with its native token, TRAC. Originally created for transparent supply chain management, OriginTrail has since expanded its scope. Today, it uses Decentralized Knowledge Graph (DKG) technology to tackle challenges like misinformation, data ownership, intellectual property rights, and growing inaccuracies in AI usage. The DKG acts as a knowledge base that verifies data through blockchain, while the TRAC token is used for staking, payments, and rewards.
- VitaDAO: With its native token VITA, the project allows members to propose, vote on, and fund cutting-edge biotechnology research focused on extending human healthspan. Launched in 2021, VitaDAO operates as a decentralized autonomous organization where members collaboratively evaluate, fund, and govern early-stage biotech projects. According to the official website, VitaDAO has raised over $4.2 million to support 24 research initiatives.
- Research Hub: Also called a GitHub for Science, ResearchHub aims to accelerate scientific progress by providing a modern platform where researchers can collaborate efficiently. The platform allows scientists to publish articles, both preprints and postprints, and openly discuss findings in dedicated forums for each paper. This approach makes sharing and reviewing research faster and more transparent. ResearchHub uses its native token, ResearchCoin (RSC), to reward users who contribute by sharing papers, reviewing work, or engaging in discussions.
- Bio Protocol: Designed to improve trust in scientific research, BioProtocol uses blockchain to store and verify research methods and protocols. This ensures experiments are clear and can be repeated. Researchers can safely share their work and record when it was done. The platform’s native cryptocurrency, the BIO token, rewards contributors for sharing and checking protocols, encourages community involvement, and lets token holders help make decisions. This helps promote open, reliable, and high-quality science.
Where Is Decentralized Science Headed Next?
Decentralized science is growing fast, and the future looks promising. One big shift is the combination of blockchain and AI to make research more open, trustworthy, and easier to manage. Smart contracts automate funding and collaboration through DAOs.
Another key trend is the rise of DeSci tokens, which reward people who contribute to research and help scientists around the world access funding without relying on traditional systems. These tokens also support fair ownership and profit-sharing.
We’ll likely see more cross-disciplinary teamwork, as DeSci platforms connect experts from around the world to solve big problems faster. Regulations may also begin to evolve to support these new approaches to science.
Despite challenges around adoption and regulation, DeSci represents a fundamental shift toward more open, transparent, and collaborative scientific research. As these platforms mature and gain adoption, they could reshape how humanity approaches scientific discovery and innovation.
Content on BlockPort is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial guidance.
We strive to ensure the accuracy and relevance of the information we share, but we do not guarantee that all content is complete, error-free, or up to date. BlockPort disclaims any liability for losses, mistakes, or actions taken based on the material found on this site.
Always conduct your own research before making financial decisions and consider consulting with a licensed advisor.
For further details, please review our Terms of Use, Privacy Policy, and Disclaimer.




























