Blockchain technology in finance

Blockchain is no longer just about crypto. From cross-border payments to asset management, blockchain in finance industry shows how decentralized systems cut costs, reduce risks, and open new opportunities for banks, investors, and businesses worldwide.
Blockchain technology in finance is transforming the way financial institutions operate, making processes faster, more transparent, and less dependent on intermediaries. Originally designed as the backbone of digital currencies, it is now driving innovation in payments, capital markets, asset management, and global trade. By enabling secure data sharing and smart contract automation, blockchain reduces costs, minimizes risks, and sets the stage for a more efficient financial ecosystem.
Key advantages of blockchain technology in the financial sector
Blockchain applications in finance bring three core benefits. First is transparency: every participant sees the same ledger, making fraud and errors far less likely. Second is automation: smart contracts cut out middlemen and execute deals when preset rules are met. Third is efficiency: transactions settle in minutes instead of days, reducing both cost and friction. On top of that, cryptography keeps data secure and builds trust between parties.
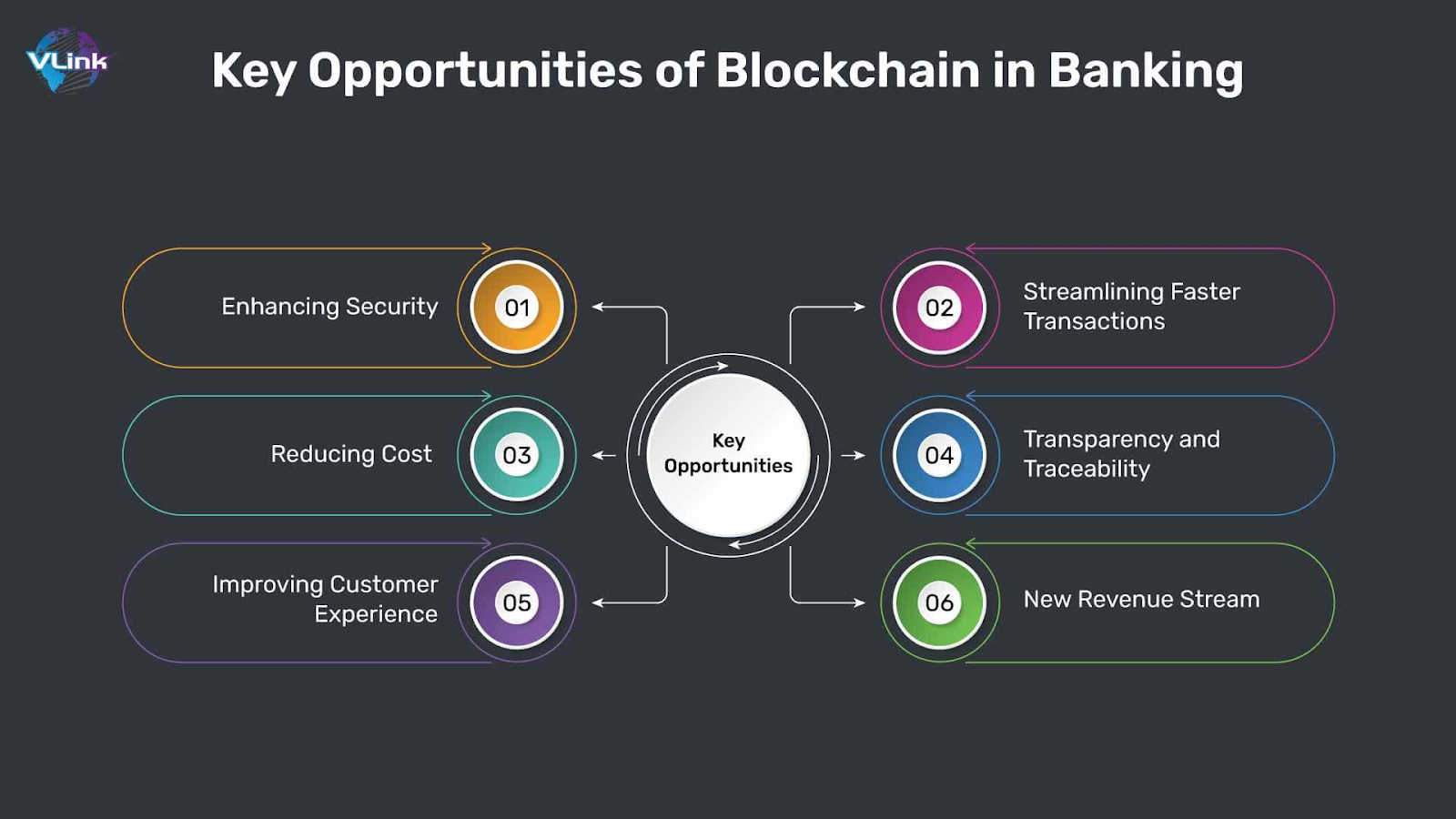
These foundational benefits manifest across multiple areas of financial services, from asset digitization to everyday payment processing.
The Role of Digitalization of Financial Assets in Transforming Finance
Digitization of assets is changing how we see blockchain and finance. Traditional securities, loans, or even real estate can be turned into tokens that move instantly on-chain. This unlocks faster settlement, fractional ownership, and broader investor access. For issuers, it means lower costs and new ways to design products. For investors, it means more liquidity and transparency in markets that used to be closed or slow.
The mechanics behind this transformation: involve converting legal rights into programmable digital tokens. When a real estate property becomes tokenized, each token represents a fractional ownership stake with embedded rights to rental income, voting on property decisions, and capital appreciation. Unlike traditional REITs, these tokens can trade 24/7 on blockchain platforms without traditional market hours or intermediary delays.
Real-world momentum is accelerating. JPMorgan has processed over $300 billion in tokenized repo transactions through its JPM Coin system. Goldman Sachs completed its first tokenized bond issuance in 2024, reducing settlement time from days to minutes. Meanwhile, platforms like tZERO and Polymath enable companies to issue compliant security tokens that retain regulatory protections while gaining blockchain efficiency.
The implications extend beyond simple digitization. Smart contracts can automate complex corporate actions – imagine bonds that automatically adjust interest rates based on market conditions, or equity tokens that distribute dividends instantly upon earnings announcements. Investment funds can rebalance portfolios through programmatic trading rules, eliminating manual intervention and reducing costs.
Regulatory clarity is emerging as authorities recognize the potential. The EU’s Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation provides frameworks for tokenized securities, while jurisdictions like Singapore and Switzerland offer clear pathways for asset tokenization. This regulatory evolution ensures that blockchain-based assets maintain investor protections while capturing technological advantages.
However, challenges persist. Legacy financial infrastructure wasn’t designed for 24/7 blockchain operations, creating integration complexities. Legal frameworks must evolve to handle cross-border tokenized assets, and market participants need new custody and compliance solutions. Despite these hurdles, the direction is clear: asset digitization represents the next evolution in how we create, trade, and manage financial instruments.
Blockchain use cases in finance sector
The most common blockchain for financial services use cases cover payments, lending, trading, and compliance. In payments, banks use blockchain rails to settle transfers in near real time, cutting both costs and intermediaries. In lending, smart contracts automate credit scoring, collateral management, and loan execution, reducing delays from weeks to minutes.
In capital markets, tokenized securities streamline issuance and post-trade settlement, lowering risks of fraud or error. Compliance also benefits: digital identities and on-chain KYC checks speed up onboarding and reporting. Together, these cases show that blockchain is no longer just an experiment but a working layer of modern finance.
Blockchain’s influence on capital markets
Blockchain financial technology is changing how capital markets work. Settlement that once took days now happens almost instantly, removing the need for endless reconciliations. Transparency improves because every participant shares the same immutable record, making manipulation or hidden trades harder.
Costs fall as clearinghouses and custodians are replaced by automated smart contracts. At the same time, tokenization allows new ways to raise funds, from digital bonds to fractional equity. The result is a market that is faster, cheaper, and more accessible to both issuers and investors.
Blockchain’s role in modern asset management
One of the most relevant blockchain use cases in finance is asset management. Tokenization allows funds, stocks, or real estate to be split into digital units that can be traded instantly. This lowers entry barriers for investors and makes portfolios more liquid. Smart contracts handle settlements, corporate actions, and reporting with less manual work, cutting costs for managers and clients alike.
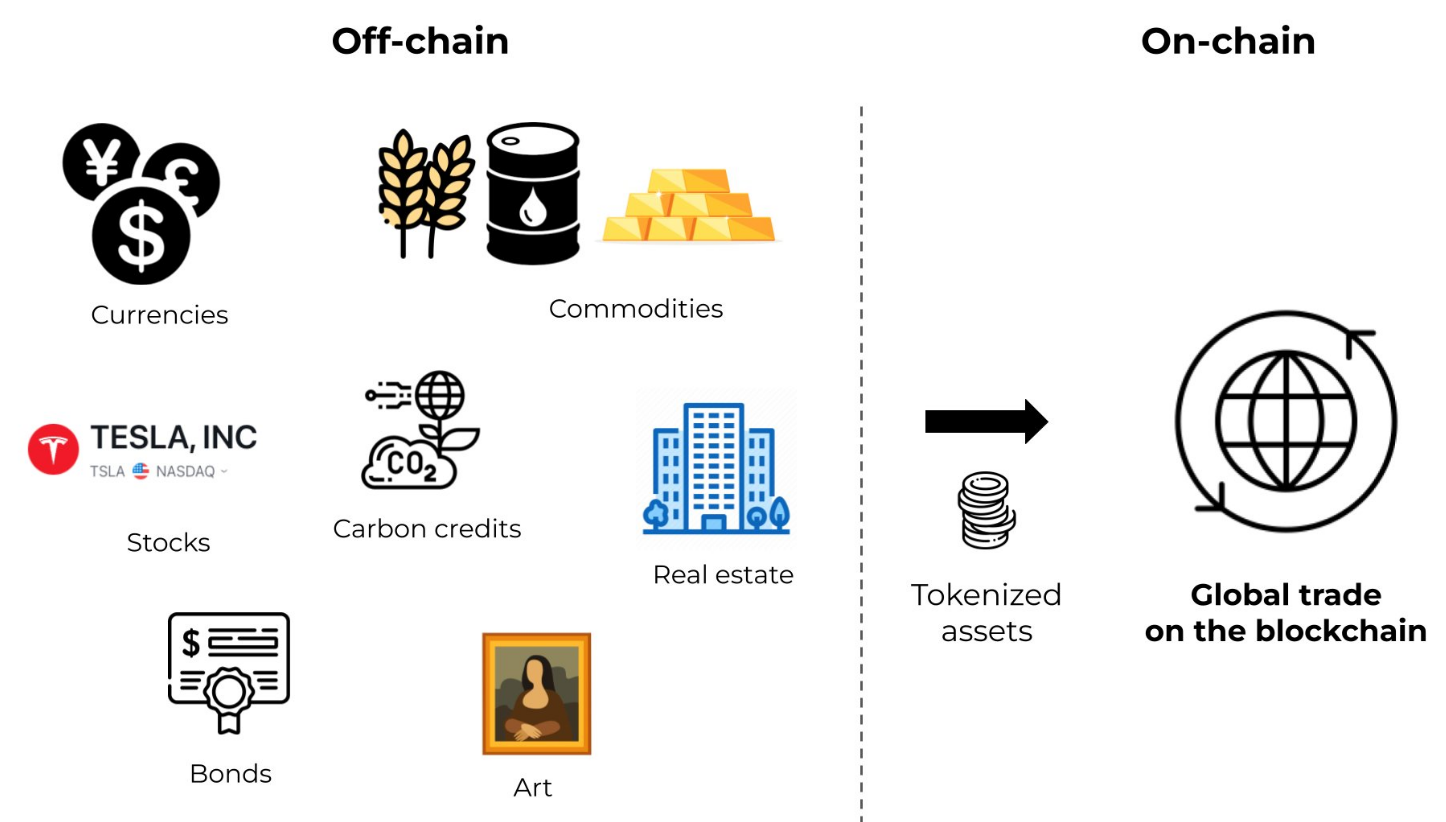
But challenges remain. Regulations are still catching up, and not all markets accept digital tokens as legal instruments. Interoperability between legacy systems and new blockchain platforms is also a hurdle. For asset managers, this means the opportunity to unlock efficiency is real, but adoption will require careful integration and compliance.
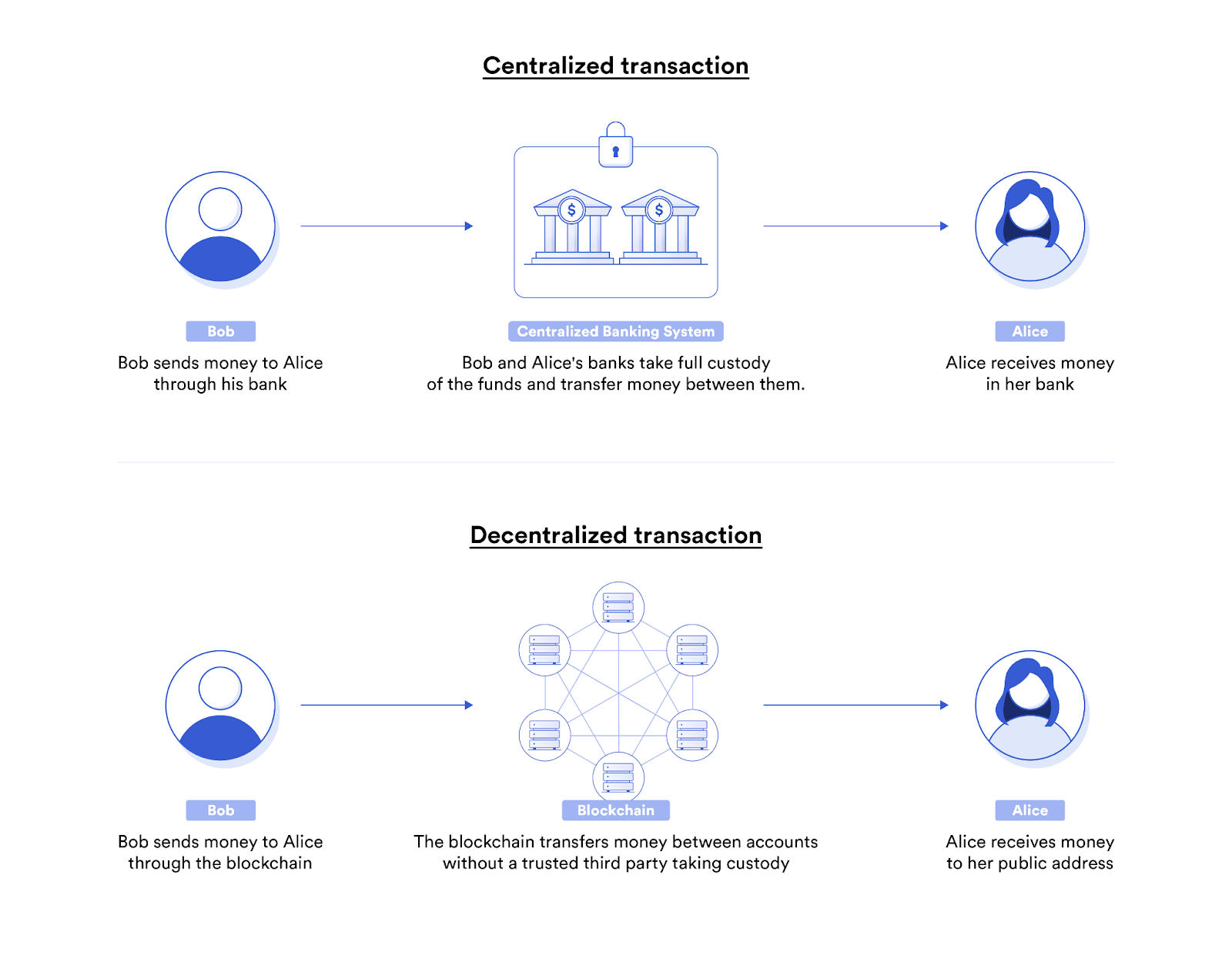
Impact of blockchain on cross-border payments and money transfers
One of the clearest links between blockchain and finance is the global money movement. Traditional cross-border payments rely on multiple intermediaries, from correspondent banks to clearinghouses. Each adds time, cost, and complexity. With blockchain, transfers move directly between participants, verified on a shared ledger without waiting days for settlement.
The impact is visible in remittances. Migrant workers sending money home often face high fees and long delays. Blockchain rails reduce fees to a fraction and deliver funds within minutes. This makes financial services more inclusive, especially in regions where access to traditional banking is limited.
For institutions, blockchain streamlines treasury operations and foreign exchange. Payments can be tracked end-to-end, giving businesses real-time visibility over cash flows. As adoption grows, blockchain could replace legacy networks like SWIFT with faster, cheaper, and more transparent systems for global transfers.
Blockchain in trade finance and international commerce
One of the strongest cases for blockchain for financial services is trade finance. Letters of credit, invoices, and shipping documents usually pass through dozens of checks, often on paper. Blockchain turns them into digital records shared in real time by banks, exporters, and importers. This cuts delays, lowers administrative costs, and reduces the chance of fraud.
In international commerce, the same technology improves trust between trading partners. Smart contracts can release payments automatically when goods reach a port, while regulators gain clearer visibility into transactions. By making processes faster and more reliable, blockchain helps global supply chains move with less friction and more transparency.
The future of finance: beyond traditional boundaries
Blockchain technology in finance has evolved from experimental concept to operational reality, fundamentally reshaping how financial institutions approach payments, markets, and asset management. The transformation goes beyond simple efficiency gains – it’s creating entirely new financial architectures that operate with unprecedented transparency, speed, and accessibility.
The evidence is compelling: settlement times measured in minutes rather than days, cross-border payments at a fraction of traditional costs, and asset tokenization opening previously illiquid markets to global investors. These aren’t future possibilities – they’re current applications delivering measurable results.
Yet we’re still in the early stages. As regulatory frameworks mature and interoperability improves, blockchain applications in finance will expand from specialized use cases to core infrastructure. The institutions that master this technology today won’t just optimize existing processes – they’ll define the operating principles of tomorrow’s global financial system.
The question isn’t whether blockchain will transform finance, but how quickly traditional institutions can adapt to this new reality before more agile competitors leave them behind.
Content on BlockPort is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial guidance.
We strive to ensure the accuracy and relevance of the information we share, but we do not guarantee that all content is complete, error-free, or up to date. BlockPort disclaims any liability for losses, mistakes, or actions taken based on the material found on this site.
Always conduct your own research before making financial decisions and consider consulting with a licensed advisor.
For further details, please review our Terms of Use, Privacy Policy, and Disclaimer.

























